Vapor Pressure And Imf Relationship
pressure relationshipA substance enclosed in a sealed vessel initially at vacuum no air inside will quickly fill any empty space with vapor. Determine the dominant IMF present in nitrogen triodide.
 Intermolecular Forces And Vapor Pressure Video Khan Academy
Intermolecular Forces And Vapor Pressure Video Khan Academy
Vapor pressure and IMF Vapor Pressure and Boiling Point When you heat a liquid the particles in the liquid absorb the heat which increases the kinetic energy.
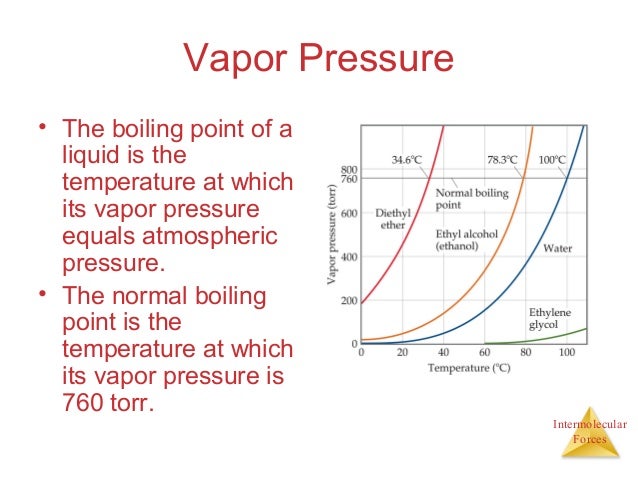
Vapor pressure and imf relationship. IMF stands for InterMolecular Forces. Here is the best explanation share if you like it. On the other hand there is a difference in temperature between evaporation versus boiling.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The relationship between vapor pressure and IMF strength in water. What is the relationship between temperature versus vapor pressure.
IMF strength and surface tension are directly related. Both evaporation and boiling involves a molecule in the liquid state becoming a molecule in the gas state which requires energy to overcome the IMF. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
That is the amount of force with which the molecules of a substance are attracted to each otherr. In fact with a boiling point of -19 C formaldehyde exists as a gas at room temperature while methanol exists as a liquid Exercise 24. A bird is covered in oil from a big spill.
C The stronger are the IMF the higher is vapor pressure. The molecules leaving a liquid through evaporation create an upward pressure as they collide with air molecules. To know how and why the vapor pressure of a liquid varies with temperature.
Part B What is the relationship between the intermolecular forces in a solid and its melting point. The vapor pressure of a liquid is the equilibrium pressure of a vapor above its liquid or solid. To understand that the equilibrium vapor pressure of a liquid depends on the temperature and the intermolecular forces present.
Higher the inter-molecular forces lower will be the vapour pressure of a liquid. What is the basis of your response. Into the vapor phase ie you need more energy to convert it from liquid to the vapor phase in other words higher its boiling point.
IMF strength and vapor pressure volatility are inversely related. Formaldehyde with weaker IMF should have a higher vapor pressure. Weak intermolecular forces produce a higher rate of evaporation and a higher vapor pressure.
If the IMFs are high that means the molecules are strongly. Start studying Chem Chap. What is the best treatment to save the bird.
A They are not related at all. Vapor pressure is a measurement of how readily a condensed phase forms a vapor at a given temperature. This upward push is called the vapor pressur.
As the temperature increases the vapor pressure increases. After the system reaches equilibrium and no more vapor is formed this vapor pressure can be measured. In other words the substance comes in direct contact with the pressure measurement device since there is no intervening open-end manometer.
Because hydrogen bonding is the strongest type of IMF we would expect methanol to have stronger IMF than formaldehyde. The increase in the kinetic energy allows more particle to enter the gas phase. B The stronger are the IMF the lower is vapor pressure.
Relationship between Vapor Pressure and Boiling Point Substances that have high vapor pressure vaporize easily have lower boiling points than substances that have low vapor pressure do not vaporize easily and have higher boiling points Weak IMF àHigh vapor pressure àlow boiling point Strong IMF àLow vapor pressure àhigh boiling point. Vapor pressure of a liquid is Inversely proportional to inter-molecular forces of attraction. If it is harder for a liquid to escape into vapor because it is held back into the liquid by the neighboring particles attraction you have less vapor and hence low vapor pressure.
Vapor Pressure 2 In a vacuum line the vapor pressure of the substance is directly measured by the pressure transducer. D It depends on the temperature at which those liquids all are. That is the pressure of the vapor resulting from evaporation of a liquid or solid above a sample of the liquid or solid in a closed container.
Therefore most of the vapor is at a different temperature than the liquid. To understand that the relationship between pressure enthalpy of vaporization and temperature is given by the Clausius-Clapeyron equation. What is the relationship between IMF strength and vapor pressure.
Type of IMF in a molecule of NH3. Strong intermolecular forces produce a lower rate of evaporation and a lower vapor pressure.